Understanding Galvanizing: The Process, Benefits, and Applications
In the world of materials science and manufacturing, protecting metals from corrosion is essential for durability and performance. Galvanizing, one of the most popular and effective methods, involves coating steel with a layer of zinc to protect it from environmental degradation. This blog will explore the science behind galvanizing, its various applications, benefits, and why it remains crucial in industries like automotive, construction, and manufacturing.
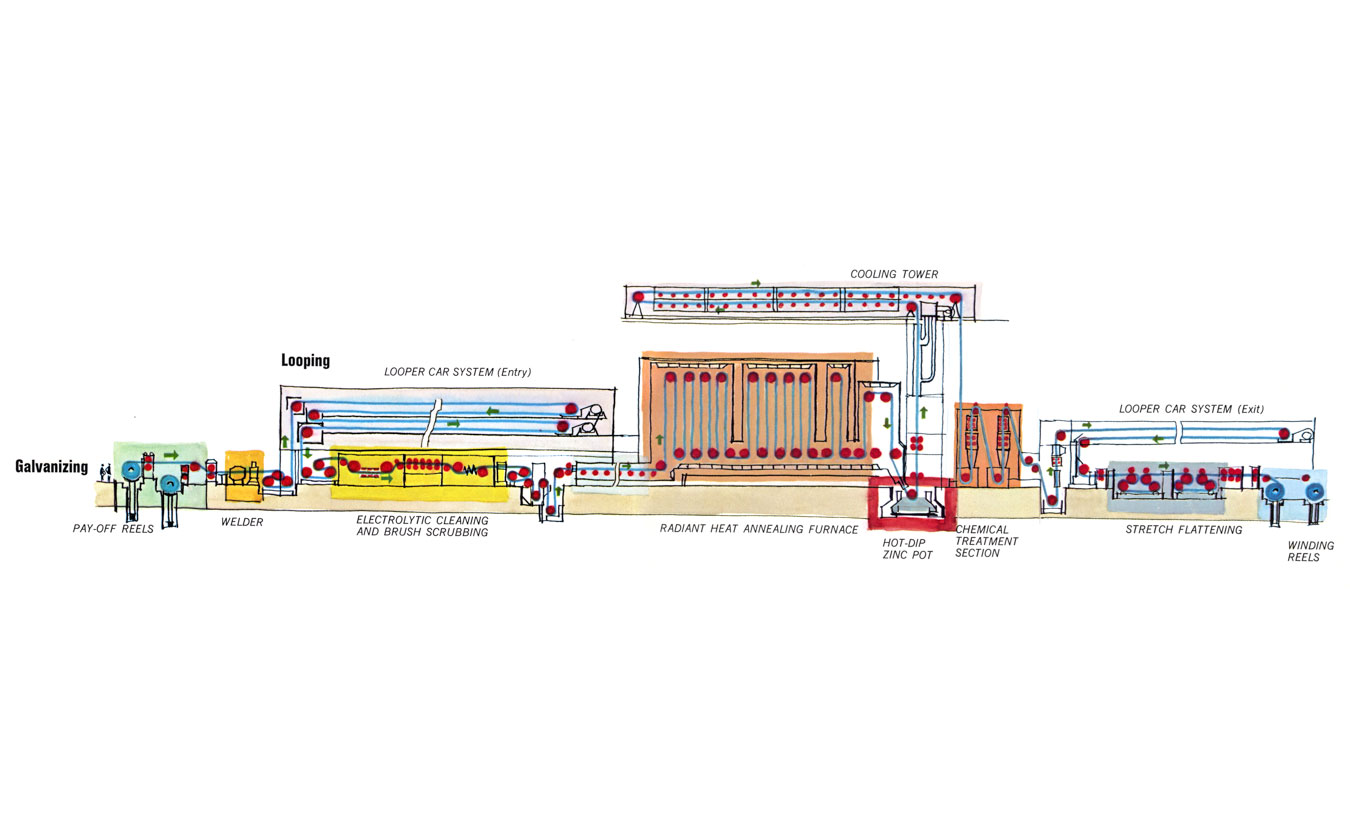
What is Galvanizing?
Galvanizing is the process of applying a thin layer of zinc to the surface of steel or iron. This layer acts as a protective barrier against corrosion, prolonging the lifespan of the metal. When exposed to the environment, metals like steel are susceptible to oxidation, which leads to rust and gradual degradation. The zinc coating shields the steel, preventing direct exposure to moisture and oxygen, the two primary catalysts of corrosion.
The zinc layer in galvanized steel provides protection in two ways:
Barrier Protection
The zinc coating creates a physical barrier that prevents corrosive elements from reaching the steel surface.
Sacrificial Protection
Zinc is more reactive than steel, meaning it corrodes first, thereby "sacrificing" itself to protect the underlying metal. This dual-layered protection ensures that even if the coating is scratched, the exposed area remains shielded from rapid corrosion due to the zinc’s sacrificial nature.
Types of Galvanizing Processes
There are several methods for galvanizing steel, each suited for different applications and types of materials. The most common methods include:
Hot-Dip Galvanizing
This is the most widely used galvanizing process. Steel parts are dipped into a bath of molten zinc, which forms a strong bond with the steel. Hot-dip galvanizing is ideal for larger steel structures and is commonly used in the construction industry.
Electrogalvanizing
In this method, an electric current is used to apply a thin layer of zinc to the steel surface. The electroplated layer is typically thinner than in hot-dip galvanizing, making it suitable for applications requiring a smooth finish, such as in the automotive industry.
Galvannealing
A process combining hot-dip galvanizing and annealing, galvannealing is typically used for automotive parts. The zinc coating is heated to create a smooth and paintable surface, which improves adhesion and durability.
Thermal Spray Galvanizing
In this process, zinc wire or powder is melted and sprayed onto the steel surface. It is used for on-site galvanizing and for structures that cannot be dipped in molten zinc.
Benefits of Galvanizing Steel
Galvanizing steel offers several significant advantages, which makes it a preferred choice across various industries. Here are some of the key benefits:
Corrosion Resistance
Galvanizing provides long-lasting protection against rust and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor structures and environments exposed to harsh weather conditions.
Cost-Effective Protection
Compared to other corrosion-resistant treatments, galvanizing is relatively inexpensive, offering a cost-effective solution for manufacturers and builders.
Low Maintenance
Galvanized steel requires minimal maintenance, reducing long-term costs associated with repairs and replacements.
Longevity
The lifespan of galvanized steel can extend up to 50 years in rural environments and up to 25 years in urban and coastal environments, depending on exposure conditions.
Complete Coverage
The galvanizing process ensures a uniform coating, covering all surfaces, edges, and corners of the steel, even hard-to-reach areas.
Quick Application
Galvanizing is a straightforward process that can be applied quickly, making it efficient for large-scale production and construction projects.
Applications of Galvanized Steel
Due to its durability and resistance to corrosion, galvanized steel is used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the prominent applications include:
Automotive Industry
Galvanized steel is extensively used in the automotive sector, especially for car bodies and parts exposed to moisture and salt. Galvanized sheets help prevent rust and ensure the longevity of vehicle frames, fuel tanks, and exhaust systems. Additionally, the lightweight nature of galvanized steel supports fuel efficiency.
Construction and Infrastructure
In construction, galvanized steel is commonly used in roofing, fencing, handrails, and structural frameworks. Its resistance to weathering and rust makes it ideal for bridges, power towers, and pipelines. Galvanized steel’s durability and ability to withstand outdoor elements make it a preferred material for long-term structural projects.
HVAC Systems
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on galvanized steel for ductwork and air handling units. The corrosion-resistant properties of galvanized steel ensure the systems remain free from rust, reducing maintenance and ensuring clean airflow within buildings.
Agriculture and Livestock
In agriculture, galvanized steel is used to manufacture structures like barns, sheds, and silos. It is also used for fencing and livestock pens, providing durability against environmental exposure and wear from animals.
Household Appliances
Galvanized steel is found in household appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, and microwaves. The zinc coating protects these appliances from moisture and extends their lifespan, ensuring that they remain reliable and safe to use.
Electrical and Utility Poles
Utility poles, transmission towers, and electrical enclosures are commonly constructed with galvanized steel. This application benefits from galvanizing’s resistance to harsh weather conditions and the elements, ensuring long-term stability and safety.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Galvanizing
Galvanizing is an environmentally friendly process for several reasons:
- Recyclability: Galvanized steel is fully recyclable, and both steel and zinc can be reused without losing their properties.
- Reduced Maintenance: The long lifespan and low maintenance requirements of galvanized steel reduce resource consumption, resulting in less waste over time.
- Zinc Recovery: During the galvanizing process, excess zinc can be recovered and reused, minimizing waste and conserving resources.
Galvanized steel’s durability and recyclability contribute to sustainability in construction and manufacturing, supporting a more eco-friendly approach to material usage.
Final Thoughts
Galvanizing is an effective, economical, and eco-friendly process that protects steel from corrosion. Its versatility and durability have made it an essential part of industries ranging from automotive to construction, agriculture, and beyond. The use of galvanized steel helps reduce long-term maintenance costs and supports sustainable practices due to its recyclability.
Whether in the automotive sector, HVAC systems, or agricultural applications, galvanized steel continues to play a pivotal role in modern infrastructure and manufacturing. By understanding the benefits and applications of galvanizing, industries can make informed decisions to enhance product longevity, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact.
